
WTL Varde
Reusing data centre waste heat for vegetable production in greenhouses
Together with atNorth, a leading Nordic data centre developer, WA3RM plans to develop a new project in the municipality of Varde on the Danish west coast. The data centre campus, called DEN02, will have an initial capacity of 250MW and excess heat from the site will be recycled with WA3RM as part of a state-of-the-art greenhouse development for vegetable production. The total area for the data centre and greenhouse project covers 174 hectares.
Later this year we will begin to work on the second greenhouse. Paired with Greenhouse 1 this will provide a big boost to Sweden’s domestic production of tomatoes, reaching a total of around 17,000 tonnes of annual production – about every fifth tomato eaten in Sweden.
Varde Project
Pre-study phase
Anchor industry
Data center
Waste stream
Heat
Application
Greenhouse
Vegetable
TBD
Greenhouse size
30 – 40 ha
Investment (€)
123
Production start
TBD
Later this year we will begin to work on Greenhouse 2. Paired with Greenhouse 1 this will provide a big boost to Sweden’s domestic production of tomatoes, reaching a total of around 17,000 tons of annual production – about every fifth tomato eaten in Sweden.
Vegetable production in modern greenhouses using residual heat addresses many of the problems that exist in today's food production around the world, such as water scarcity and emissions from fossil fuel heating.
A project like this can redefine the Nordic food landscape. By slashing emissions from heating and transportation and, dramatically reducing water consumption, this initiative represents a more responsible approach to food production.
Sources: McKinsey & Company, The energy transition: A region-by-region agenda for near-term action, December 15, 2022.UN World Water Development Report 2023 Ipcc:fao/WHO. Global Data, 2022 https://www.unesco.org/reports/wwdr/2023/en/food-and-agriculture
1/3
of global CO2-emissions comes from food production
56 %
more food needed by 2050 to feed 10 billion people
72 %
of fresh water withdrawal comes from agriculture
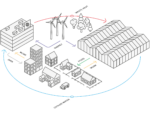
How it works
Vegetable production using waste heat
With a surplus of renewable energy in the area, and a perfect position to shorten distance from farm to fork, Varde municipality has the potential to grow a new center for vegetable production.
Increasing domestic food production reduces export dependency and makes the food system more resilient.
Growing near the end consumer and heating the greenhouse with residual heat instead of oil or gas help avoid emissions.
This project will create new jobs the associated benefits that come with that for both individuals and communities.
Compared to growing tomatoes in the field, water usage per tomato grown is up to 90% lower in a hydroponic greenhouse.
Documents

Meeting needs for computing power and resource-efficient food production all at once
Challange
The rapid growth of AI technologies is driving an increased demand for data centers, as vast computational power is required to support machine learning, data processing, and cloud-based services. Simultaneously, the global need for food production is rising, with an urgent push to grow more with fewer resources.
Innovative solutions, such as using excess heat from data centers to power sustainable agricultural projects, offer a way to address both challenges. By integrating data infrastructure with resource-efficient food production, we can reduce environmental impact and create a more sustainable future.
UN Sustainability Development Goals addressed:
8.2 Achieve higher levels of economic productivity through diversification, technological upgrading and innovation, including through a focus on high-value added and labour-intensive sectors.
8.3 Promote development-oriented policies that support productive activities, decent job creation, entrepreneurship, creativity and innovation, and encourage the formalization and growth of micro-, small- and medium-sized enterprises, including through access to financial services. Improve progressively, through 2030, global resource efficiency in consumption and production and endeavour to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation, in accordance with the 10-Year Framework of Programmes on Sustainable Consumption and Production, with developed countries taking the lead.
8.4 Improve progressively, through 2030, global resource efficiency in consumption and production and endeavour to decouple economic growth from environmental degradation, in accordance with the 10-Year Framework of Programmes on Sustainable Consumption and Production, with developed countries taking the lead.
8.8 Protect labour rights and promote safe and secure working environments for all workers, including migrant workers, in particular women migrants, and those in precarious employment.
9.4 By 2030, upgrade infrastructure and retrofit industries to make them sustainable, with increased resource-use efficiency and greater adoption of clean and environmentally sound technologies and industrial processes, with all countries taking action in accordance with their respective capabilities.
11.a Support positive economic, social and environmental links between urban, peri-urban and rural areas by strengthening national and regional development planning.
12.2 By 2030, achieve the sustainable management and efficient use of natural resources.
13.1 Strengthen resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related hazards and natural disasters in all countries.
14.1 By 2025, prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds, in particular from land-based activities, including marine debris and nutrient pollution.
15.1 By 2020, ensure the conservation, restoration and sustainable use of terrestrial and inland freshwater ecosystems and their services, in particular forests, wetlands, mountains and drylands, in line with obligations under international agreements
15.5 Take urgent and significant action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the loss of biodiversity and, by 2020, protect and prevent the extinction of threatened species.
17.16 Enhance the Global Partnership for Sustainable Development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilize and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources, to support the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals in all countries, in particular developing countries.
Project partners



FAQ
More questions?

Tomatoes from our greenhouse project in Frövi are available in store all over Sweden.

Welcoming Food Ventures
Operator
The greenhouses in Frövi will be operated by Food Ventures. A global leader in greenhouse growing, specialized in continuously supplying fresh and tasty vegetables, grown sustainably in high-tech greenhouses.
















